Bitcoin’s emergence in 2009 marked a revolutionary moment in financial history, introducing the world’s first decentralized digital currency. Its advent was not just a breakthrough in monetary terms but also a challenge to traditional concepts of financial security. Unlike traditional banking systems, Bitcoin operates on a decentralized network, relying on blockchain technology to record and verify transactions. This decentralization posed unique security challenges, necessitating novel measures to safeguard users’ digital assets.
Early Security Protocols in Bitcoin
In its infancy, Bitcoin’s security was rudimentary, primarily relying on the inherent security features of its blockchain technology. The blockchain is a public ledger, transparent and immutable, making it resistant to tampering and fraud. Every transaction on the Bitcoin network is verified by a consensus of network participants, known as miners, making fraudulent transactions difficult to execute.
However, the early days of Bitcoin were not without vulnerabilities. The nascent technology had not yet been tested against sophisticated cyber threats, and its user base, mostly tech enthusiasts and early adopters, were navigating uncharted waters in digital asset security.
The Decentralized Nature of Bitcoin and its Implications for Security
The decentralized nature of Bitcoin brought both strengths and vulnerabilities. On the one hand, decentralization meant there was no central point of failure, unlike traditional banks that could be targets for hacking and fraud. On the other hand, this lack of centralized authority meant that users were entirely responsible for the security of their Bitcoin wallets.
This responsibility led to the early adoption of basic security practices such as secure wallet backup, encryption, and awareness of phishing scams. These practices were crucial for users to protect their private keys, the critical component for accessing and transacting with their Bitcoin.
The Genesis of Bitcoin Security: Basic Protective Measures
In the early stages of Bitcoin, when the landscape of digital currencies was still taking shape, the focus on security was fundamentally about safeguarding private keys and ensuring transaction integrity. These initial measures, although basic, were pivotal in establishing a foundation for more complex security solutions that would evolve over time.
Initial Security Measures and Their Effectiveness
Bitcoin’s initial security revolved around two key aspects: securing the wallet and protecting the network. Wallet security primarily involved encrypting the wallet with a strong password. This encryption was crucial for protecting the private keys stored in the wallet, which are essential for accessing and transacting Bitcoin. Furthermore, early adopters were encouraged to maintain regular backups of their wallets to prevent loss of funds due to hardware failure or other accidents.
On the network side, Bitcoin’s security was intrinsically tied to its blockchain technology. The blockchain’s decentralized nature and reliance on a proof-of-work consensus mechanism made it inherently secure against tampering and fraud. Each transaction was verified by network nodes, and once confirmed, it became a permanent part of the blockchain ledger, resistant to alteration.
The Role of the Bitcoin Community in Enhancing Security

The Bitcoin community played a vital role in shaping these early security measures. In the absence of a centralized authority, community forums and discussions became the primary source of knowledge and best practices for security. Early adopters shared their experiences and tips, helping to educate new users about the importance of security in managing digital assets.
These community-driven efforts were instrumental in establishing a culture of security awareness within the Bitcoin ecosystem. Users learned to be cautious of potential threats like phishing attacks and malware, and the importance of using reputable software and services for managing their Bitcoin.
The Rise of Hardware Wallets and Cold Storage Solutions
As Bitcoin’s popularity soared, so did the need for more secure ways to store digital assets. This led to the emergence and widespread adoption of hardware wallets and cold storage solutions, significantly enhancing the security of Bitcoin holdings.
How Hardware Wallets Revolutionized Security
Hardware wallets are physical devices designed to securely store cryptocurrency offline. They are immune to online hacking attempts, as they do not expose private keys to the internet. Key features of hardware wallets include:
- Physical Security: Private keys are stored in a secure chip and never leave the device.
- Pin Protection: Access to the wallet is protected by a PIN, adding an extra layer of security.
- Backup and Recovery: Users can back up their wallet with a recovery phrase, allowing for easy recovery of funds in case the device is lost or damaged.
Popular hardware wallets like Ledger and Trezor became synonymous with security in the Bitcoin ecosystem, offering users peace of mind.
Cold Storage Methods and Their Importance
Cold storage refers to keeping a reserve of Bitcoin offline. This method includes not only hardware wallets but also paper wallets and other forms of secure offline storage. The importance of cold storage lies in its ability to provide security against online threats such as hacking, phishing, and other cyber attacks. Here’s why cold storage gained prominence:
- Enhanced Security: Storing Bitcoin offline significantly reduces the risk of theft from online breaches.
- Control Over Funds: Users have full control over their private keys and, consequently, their funds.
- Long-term Storage: Cold storage is ideal for long-term investors or ‘HODLers’ who do not require frequent access to their Bitcoin.
Multi-Signature Wallets: An Additional Layer of Security
The evolution of Bitcoin security saw the introduction of multi-signature (multi-sig) wallets, an innovation that added an extra layer of security for users. Multi-sig technology requires multiple private keys to authorize a Bitcoin transaction, significantly reducing the risk of theft or unauthorized access.
The Concept and Working of Multi-Signature Wallets
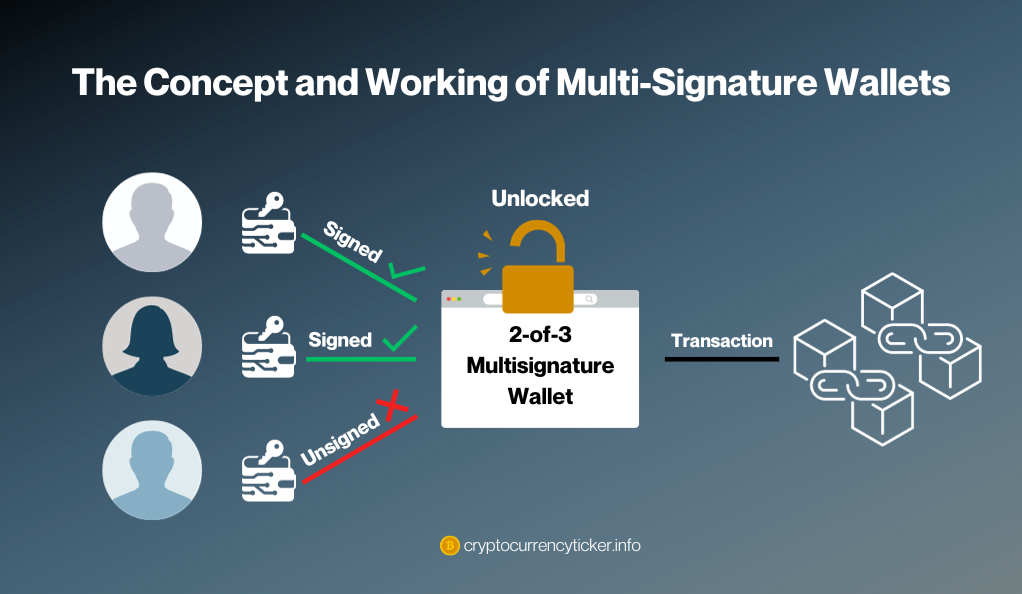
Multi-sig wallets operate on the principle that no single individual or device holds complete control over the funds. These wallets require more than one private key to sign and approve a transaction. Typically, a multi-sig wallet setup involves:
- Multiple Keyholders: Involves two or more parties (individuals, devices, or services) each holding a unique private key.
- Transaction Approval Process: A transaction is only processed if a predefined number of keys (e.g., 2-of-3, 3-of-5) sign off on it.
This mechanism ensures that even if one key is compromised, the funds remain secure, as unauthorized transactions cannot be processed without the required number of signatures.
How Multi-Signature Technology Bolsters Bitcoin Security
Multi-sig technology enhances Bitcoin’s security in several ways:
- Mitigation of Single Point of Failure: By distributing control among multiple keys, multi-sig reduces the risk associated with a single point of failure.
- Ideal for Shared Control: It’s especially useful for organizations or groups where funds need to be accessed by multiple individuals.
- Enhanced Security for Service Providers: Exchanges and wallet services use multi-sig to secure customer funds, adding an extra layer of security against internal fraud or external breaches.
Decentralized Exchanges and Enhanced Security Protocols
The evolution of Bitcoin security also witnessed the rise of decentralized exchanges (DEXs). These platforms, unlike traditional centralized exchanges, allow users to trade cryptocurrencies directly with each other, without the need for an intermediary. This decentralization has significant implications for security.
The Shift to Decentralized Exchanges and Its Security Benefits
Decentralized exchanges offer several security advantages over their centralized counterparts:
- Reduced Risk of Centralized Attacks: Without a central point of control, DEXs are less vulnerable to the kind of large-scale hacks that have plagued centralized exchanges.
- User Control Over Funds: Users of DEXs maintain control over their private keys, which means they have full control over their funds. This eliminates the risk associated with entrusting funds to a third party.
- No Single Point of Failure: The distributed nature of DEXs means there is no single point of failure, enhancing overall system resilience.
New Protocols in Decentralized Exchanges for Improved Security
In addition to their inherent security features, many decentralized exchanges have started implementing advanced security protocols:
- Smart Contract-Based Trading: DEXs often use smart contracts to facilitate trades, which can automate and secure transactions without human intervention.
- Liquidity Pools: Some DEXs use liquidity pools to facilitate trading, which can reduce the risk of market manipulation and increase the security of trades.
- Privacy Features: Many DEXs incorporate privacy-enhancing features, such as anonymous trading, which can protect user identities and transaction details.
Smart Contract Audits and Layered Defense Mechanisms
As Bitcoin’s ecosystem matured, the adoption of smart contracts and the need for layered defense mechanisms became increasingly important. These elements play a critical role in enhancing the security of the entire Bitcoin network.
The Role of Smart Contract Audits in Preventing Vulnerabilities

Smart contract audits are thorough examinations of the code underlying smart contracts, conducted by security experts. These audits are crucial for several reasons:
- Identifying Flaws and Vulnerabilities: Auditors scrutinize smart contract codes for potential security flaws, which could be exploited by attackers.
- Ensuring Compliance with Best Practices: Audits check for adherence to coding best practices, reducing the likelihood of bugs and other issues.
- Building Trust: Successfully audited contracts provide a sense of security to users, enhancing trust in the platform or application.
Layered Defense Strategies in the Bitcoin Ecosystem
The concept of layered defense, or defense in depth, involves implementing multiple layers of security controls throughout an information system. In the context of Bitcoin, this might include:
- Network Security Measures: Such as firewalls and intrusion detection systems to protect the infrastructure supporting Bitcoin transactions and wallets.
- Transaction Monitoring: Continuous monitoring of transactions for suspicious activities to prevent fraud and other malicious activities.
- Education and Awareness: Providing users with the knowledge and tools to secure their own wallets and transactions.
Future Horizons: Preparing for Quantum-Resistant Algorithms
The ongoing evolution of Bitcoin security is not just about addressing current threats but also preparing for future challenges, particularly the potential impact of quantum computing.
The Potential Threat of Quantum Computing to Bitcoin Security
Quantum computing poses a significant threat to cryptographic algorithms used in Bitcoin, especially concerning the security of private keys. Quantum computers, with their advanced computational capabilities, could theoretically break the cryptographic algorithms that currently secure Bitcoin transactions and wallets.
The Development of Quantum-Resistant Algorithms and What It Means for Bitcoin
In response to this emerging threat, there is an ongoing effort to develop quantum-resistant algorithms. These algorithms aim to be secure against the capabilities of quantum computers. Key developments include:
- Post-Quantum Cryptography: Research and development of cryptographic algorithms that are secure against both quantum and classical computers.
- Blockchain Protocols Enhancements: Modifying existing blockchain protocols to incorporate post-quantum cryptographic algorithms.
- Community and Research Collaboration: Collaboration between academic researchers, cryptographers, and the Bitcoin community to stay ahead of quantum computing threats.
Conclusion
The evolution of Bitcoin’s security mirrors its growth and the broader digital currency landscape. From initial basic measures to today’s advanced defenses, Bitcoin has shown remarkable adaptability in addressing security challenges. As the cryptocurrency world continues to evolve, particularly with potential quantum computing threats, the Bitcoin community’s commitment to innovation and security remains steadfast. This journey highlights the importance of continuous improvement and vigilance in safeguarding digital assets in an ever-changing technological realm.
