In the evolving world of blockchain technology, Polkadot stands out as a beacon of innovation and versatility. Polkadot, a scalable, heterogeneous multi-chain blockchain, marks a significant leap forward in the way blockchains can interact and scale. This section delves into the foundational aspects of Polkadot, shedding light on its unique features and the groundbreaking concept of a multi-chain architecture.
The Genesis of Polkadot
Polkadot’s creation stems from a vision to enable different blockchains to communicate and share information in a trust-free fashion, thereby creating a truly interconnected network. It is not just a single blockchain; instead, it consists of a primary network known as the relay chain and numerous parallel blockchains or parachains.
Relay Chain: The Heart of Polkadot
The relay chain is Polkadot’s central chain. Its primary function is to ensure the shared security of the network and facilitate interoperability among the parachains. It is the backbone that holds the network together, enabling the various parachains to interact securely and efficiently.
Parachains: Diverse Yet Unified
Parachains are independent blockchains that connect to the relay chain, each with its unique features and use cases. They can be customized for specific applications, such as smart contracts, finance, or data storage, while benefiting from the shared security and interoperability provided by the relay chain. This sharded multichain architecture allows for a high degree of customization and scalability.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Scalability | By processing transactions on multiple chains in parallel, Polkadot eliminates bottlenecks associated with legacy networks that process transactions sequentially. |
| Interoperability | Enables different blockchains to communicate and transfer both value and data seamlessly. |
| Customization | Parachains can be developed for specific purposes and applications, offering a tailor-made blockchain solution. |
| Shared Security | The relay chain provides pooled security, ensuring that all connected parachains are uniformly secure. |
DOT Token: More Than Just a Currency
The native token of Polkadot, DOT, serves several critical functions within the ecosystem. It is not merely a currency but a token that facilitates governance, staking, and bonding. Users holding DOT tokens have a say in the future development of the network through governance mechanisms. Moreover, the staking aspect of DOT contributes to the overall security and operational efficiency of the network.
Understanding the Polkadot Network: Core Components and Structure
Polkadot’s architecture is a complex yet elegantly designed system, composed of several key components that work together to provide a robust and flexible blockchain network. This section explores these components in detail, illustrating how they contribute to the overall functionality and efficiency of the Polkadot ecosystem.
The Relay Chain: Orchestrating Harmony
At the heart of Polkadot’s architecture is the Relay Chain, responsible for the network’s shared security, consensus, and cross-chain interoperability. It coordinates the system, ensuring that the various parachains remain interconnected and secure. The Relay Chain achieves this by employing a sophisticated consensus mechanism known as Nominated Proof-of-Stake (NPoS), which selects validators to secure the network and validate the transactions.
Parachains: Specialized Chains for Diverse Needs
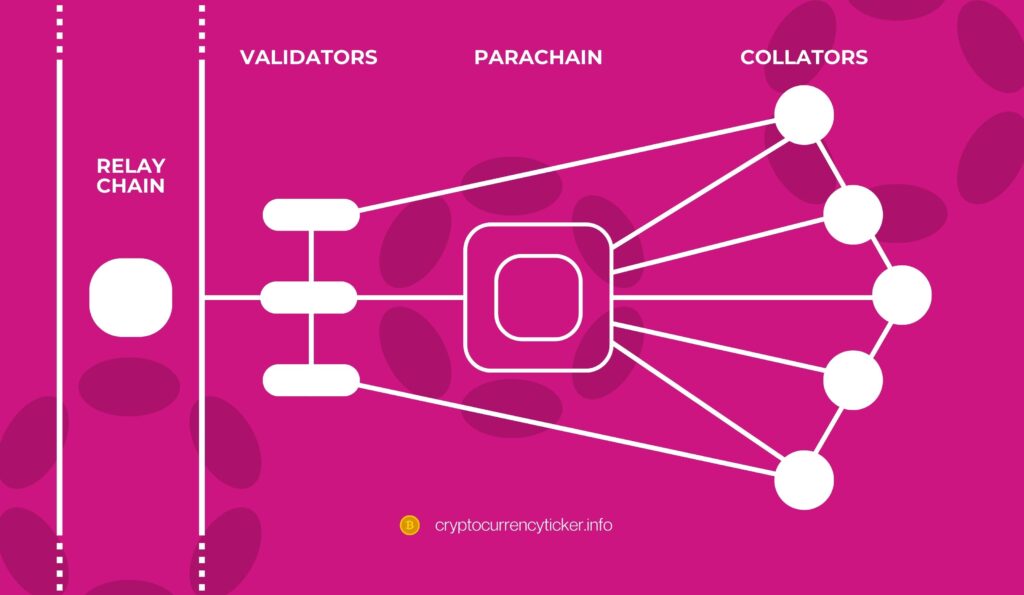
Parachains are the diverse individual blockchains that connect to the Relay Chain. Each parachain is specialized, optimized for specific use cases such as decentralized finance (DeFi), identity management, or data storage. The beauty of parachains lies in their ability to operate independently while leveraging the shared security and interoperability features of the Relay Chain. This means that while each parachain has its unique features and governance, they all benefit from the overall security and efficiency of the Polkadot network.
Cross-Chain Communication: Bridging Diverse Blockchains
One of the most notable features of Polkadot is its ability to facilitate secure and seamless communication between different blockchains. This is achieved through cross-consensus messaging (XCM), a protocol that enables the transfer of data and assets between parachains and even with external blockchains. XCM opens up a world of possibilities for interoperability, allowing various blockchain networks to interact and collaborate like never before.
The Role of DOT: Powering the Ecosystem
As mentioned earlier, the DOT token plays a central role in the Polkadot network. Beyond its use for staking and governance, DOT is also essential for bonding. When a new parachain is added to the network, a process known as bonding occurs, where a certain amount of DOT tokens are locked up to secure the parachain’s slot. This process ensures that the parachain has a vested interest in the network’s security and success.
Governance: Democratic and Decentralized
Governance on Polkadot is inherently democratic, giving stakeholders a voice in the network’s future. Decisions regarding network upgrades, protocol changes, and the addition of new parachains are made through community governance, where DOT holders can propose changes and vote on them. This ensures that the network evolves in a way that reflects the interests and needs of its community.
Innovations in Interoperability: How Polkadot Connects Diverse Blockchains
Interoperability is a cornerstone in the architecture of Polkadot, fundamentally changing how blockchains communicate and collaborate. This section explores how Polkadot achieves this feat and the implications of such connectivity in the broader blockchain ecosystem.
Breaking Down Barriers Between Blockchains
Traditionally, blockchains have operated in isolation, akin to islands with no bridges between them. This lack of connectivity has been a significant bottleneck, hindering the widespread adoption of blockchain technology. Polkadot, through its innovative design, breaks down these barriers, allowing for seamless interaction between previously incompatible networks like Bitcoin and Ethereum.
Cross-Chain Messaging: The Conduit for Interoperability
The key to Polkadot’s interoperability lies in its cross-consensus messaging (XCM) protocol. XCM acts as a universal language for blockchains, enabling the transfer of not just tokens, but any type of data or asset between parachains. This protocol extends beyond the Polkadot network, facilitating interoperability with external blockchains. This is achieved through bridges – special parachains or external networks designed to connect with other blockchains.
The Impact of Interoperability on Blockchain Ecosystem

The interoperability facilitated by Polkadot has far-reaching implications. It not only enhances the functionality of existing blockchains but also paves the way for new kinds of applications and services that can operate across multiple platforms. This interconnectedness fosters a more unified and efficient blockchain ecosystem, where the strengths of individual blockchains can be leveraged collectively.
Economic and Transactional Scalability: A Deep Dive
Polkadot’s design addresses two critical challenges in the blockchain world: economic and transactional scalability. This section examines how Polkadot achieves scalability on both fronts, enhancing the efficiency and capacity of blockchain networks.
Economic Scalability: Maximizing Efficiency
Economic scalability is about optimizing the cost and resource efficiency of blockchain operations. Polkadot achieves this by enabling a common set of validators to secure multiple blockchains. This shared security model means that individual chains do not need to maintain their own set of validators, significantly reducing the overall cost and complexity of the network. This approach not only enhances security but also lowers the barriers to entry for new blockchains, fostering a more diverse and vibrant blockchain ecosystem.
Transactional Scalability: Handling More with Less
Transactional scalability refers to a network’s ability to handle a large number of transactions efficiently. Polkadot’s sharded multichain architecture plays a crucial role here. By processing transactions on several chains in parallel (parachains), Polkadot eliminates the bottlenecks that occurred on legacy networks, which processed transactions one-by-one. This parallel processing capability allows Polkadot to handle a significantly higher volume of transactions compared to traditional blockchains.
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Economic Scalability | A common set of validators secures multiple blockchains, optimizing resource use and reducing costs. |
| Transactional Scalability | Parallel processing of transactions across multiple parachains increases throughput and efficiency. |
The Role of Parachains in Scalability
Each parachain in Polkadot is specialized and optimized for specific tasks, which means they can process transactions more efficiently than a one-size-fits-all blockchain. This specialization is key to achieving high throughput and reduced latency in the network. Furthermore, the ability to add more parachains as needed provides a scalable solution that can grow with the demands of the network.
Overcoming Legacy Network Limitations
Legacy blockchain networks often faced scalability issues due to their linear transaction processing methods. Polkadot’s multichain architecture overcomes these limitations, providing a scalable and adaptable solution. This approach not only improves transaction speed and efficiency but also ensures that the network can continue to grow and evolve without facing the scalability challenges of the past.
Layer-0 Technology: Pioneering a New Level of Security and Interoperability
Polkadot introduces the concept of a Layer-0 (L0) blockchain, a novel approach that provides a foundational infrastructure for other blockchains to build upon. This section explores what makes Polkadot a Layer-0 blockchain and how this impacts security and interoperability in the blockchain ecosystem.
Defining Layer-0 in the Blockchain Context
Layer-0 can be conceptualized as the underlying framework upon which other blockchains (Layer-1, Layer-2, etc.) can operate. Unlike Layer-1 blockchains, which are standalone networks like Bitcoin or Ethereum, Layer-0 provides the basic infrastructure and security that supports these networks. Polkadot’s Layer-0 status is pivotal in enabling it to interconnect various blockchains, both existing and new, under a unified and secure environment.
Shared Security: A Collaborative Approach
One of the defining features of Polkadot’s Layer-0 technology is shared security. In this model, the security of the entire network is pooled and distributed across all connected blockchains (parachains). This means that each parachain benefits from the collective security of the network, a feature that is particularly important for smaller or newer blockchains that may not have the resources to establish robust security independently.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Layer-0 | Provides the basic infrastructure and security layer for other blockchains to build and operate upon. |
| Shared Security | Collective security model where the security of the entire network is distributed across all connected blockchains. |
The Implications for Interoperability and Security
The Layer-0 architecture of Polkadot has significant implications for interoperability and security:
- Enhanced Interoperability: By functioning as a base layer, Polkadot enables various Layer-1 blockchains to interconnect and communicate seamlessly. This interconnectedness facilitates the transfer of data and assets across different blockchain ecosystems, enhancing their capabilities and potential applications.
- Robust Security: The shared security model ensures that even smaller blockchains can benefit from the same level of security as the larger, more established networks. This democratizes access to robust security, making it more feasible for innovative blockchain projects to emerge and thrive.
The Substrate Framework: Simplifying Blockchain Creation

Substrate, an integral part of the Polkadot ecosystem, is a powerful framework that enables developers to build custom blockchains quickly and efficiently. This section delves into the Substrate framework, its features, and how it contributes to blockchain innovation within the Polkadot network.
What is Substrate?
Substrate is a blockchain-building framework developed by Parity Technologies, designed to be highly flexible and customizable. It offers a rich set of tools and components that developers can use to create their own blockchain tailored to specific needs or use cases. Substrate is at the heart of Polkadot’s ability to support a diverse range of parachains, each with unique functionalities and characteristics.
Key Features of Substrate
- Modularity: Substrate’s modular architecture allows developers to select and compose the components they need, creating a bespoke blockchain that fits their requirements.
- Interoperability: Blockchains built with Substrate are inherently compatible with Polkadot, enabling seamless integration into the Polkadot network and interoperability with other blockchains.
- Upgradeability: Substrate-based blockchains can be upgraded without hard forks, allowing for smoother transitions and continuous improvement over time.
- Customizability: Developers have the freedom to customize various aspects of their blockchain, from the consensus mechanism to the governance model.
Accelerating Blockchain Innovation
The ease and flexibility offered by Substrate significantly lower the barriers to blockchain innovation. By providing a robust and versatile foundation, it empowers developers to experiment and innovate, leading to the creation of more diverse and specialized blockchains. This, in turn, enriches the Polkadot ecosystem, bringing a wider range of solutions and applications to the network.
Future of Polkadot: Prospects and Challenges
As we look toward the future, Polkadot stands at the forefront of the next generation of blockchain technology. This section explores the potential developments, impact, and challenges that Polkadot may encounter as it continues to evolve and shape the blockchain ecosystem.
The Growing Potential of Polkadot
Polkadot’s innovative approach to blockchain interoperability and scalability positions it as a key player in the future of decentralized technology. With its ability to connect various blockchains and create a unified network, Polkadot is well-placed to support the growing demand for interconnected blockchain applications. This could range from more efficient cross-chain DeFi solutions to new forms of decentralized governance and beyond.
Emerging Trends and Opportunities
As the blockchain sector continues to mature, we can expect to see several trends influencing Polkadot’s trajectory:
- Increased Adoption: As awareness and understanding of Polkadot’s capabilities grow, more projects are likely to adopt its technology, leading to a more robust and diverse network of interconnected blockchains.
- Innovation in Parachains: The flexibility offered by Polkadot’s parachain model is likely to spur innovation, with developers creating specialized blockchains for a wide range of applications.
- Integration with Traditional Industries: Polkadot’s interoperable and scalable framework makes it an attractive option for traditional industries looking to leverage blockchain technology, potentially leading to wider mainstream adoption.
Challenges Ahead
While the prospects for Polkadot are promising, several challenges lie ahead:
- Complexity and Usability: The complexity of Polkadot’s multi-chain architecture may pose a barrier to entry for some users and developers. Simplifying the user experience and providing comprehensive education and support will be crucial for widespread adoption.
- Competition from Other Networks: The blockchain space is highly competitive, with several projects vying for dominance in the interoperability and scalability domains. Polkadot must continue to innovate and differentiate itself to maintain its edge.
- Regulatory Landscape: The evolving regulatory environment for blockchain technology could impact Polkadot, particularly in areas like cross-chain transactions and decentralized finance.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Polkadot (DOT) stands as a transformative force in the blockchain landscape, pioneering new realms of interoperability, scalability, and innovation. Its unique multi-chain architecture, underpinned by the Relay Chain and empowered by diverse parachains, offers a scalable and secure platform for cross-chain communication and collaboration. The integration of the Substrate framework further catalyzes blockchain innovation, lowering entry barriers and fostering a fertile ground for bespoke blockchain solutions. As Polkadot navigates its path forward amidst a competitive and evolving technological landscape, it holds the potential to redefine the boundaries of blockchain capabilities, paving the way for a more interconnected and efficient digital future. The exploration of Polkadot’s features, impact, and prospects reveals not just the strengths of this pioneering platform but also the exciting possibilities it heralds for the broader blockchain ecosystem.
