In the ever-evolving world of cryptocurrency, security remains a paramount concern, especially for teams and organizations managing joint digital assets. At the forefront of innovative solutions to this challenge are multi-signature wallets, a technology that is transforming the way we think about and handle cryptocurrency security.
What is a Multi-Signature Wallet?
A multi-signature (often abbreviated as multi-sig) wallet is a type of digital wallet used for storing and managing cryptocurrencies. Unlike traditional wallets, which require just one key to authorize transactions, multi-signature wallets need multiple keys for transaction approval. This setup is akin to a safe deposit box that requires two or more keys to open, ensuring that no single individual has complete control over the wallet’s contents.
The Concept and Its Relevance
The concept of multi-signature wallets stems from the need to enhance security in the handling of cryptocurrencies. For businesses, teams, or any group managing joint funds, the risk of theft, fraud, or unauthorized access is a significant concern. Multi-signature wallets address these issues by distributing control among several parties, making it nearly impossible for any unauthorized transaction to occur without collective consent.
Key Features of Multi-Signature Wallets
- Multi-Key Approval: Transactions require the consent of multiple authorized individuals.
- Enhanced Security: Reduced risk of single points of failure, unauthorized access, and fraud.
- Decentralized Control: Promotes a more democratic and transparent decision-making process.
- Customization: The number of signatures required can be tailored to the organization’s needs.
- Audit Trails: Every transaction is transparent and traceable, reinforcing accountability.
The Rising Importance in Cryptocurrency Management
As cryptocurrency becomes increasingly integrated into the operational fabric of businesses and organizations, the relevance of multi-signature wallets continues to grow. These wallets offer a robust solution to the unique challenges posed by the management of digital assets, combining security with collaborative control.
The Technological Mechanics of Multi-Signature Wallets
Multi-signature wallets are underpinned by a fascinating blend of cryptography and blockchain technology, providing a secure and efficient way to manage cryptocurrency transactions. Understanding these mechanics is crucial for anyone looking to implement or use multi-signature wallets in their operations.
The Role of Public and Private Keys
At the heart of a multi-signature wallet lies the concept of public and private keys. These keys are cryptographic codes that enable the secure handling of cryptocurrency transactions. A public key is like an address to which others can send funds, while a private key is akin to a password that allows the owner to access and use these funds. In a multi-signature setup, each participant has their own set of these keys.
How Multi-Signature Works
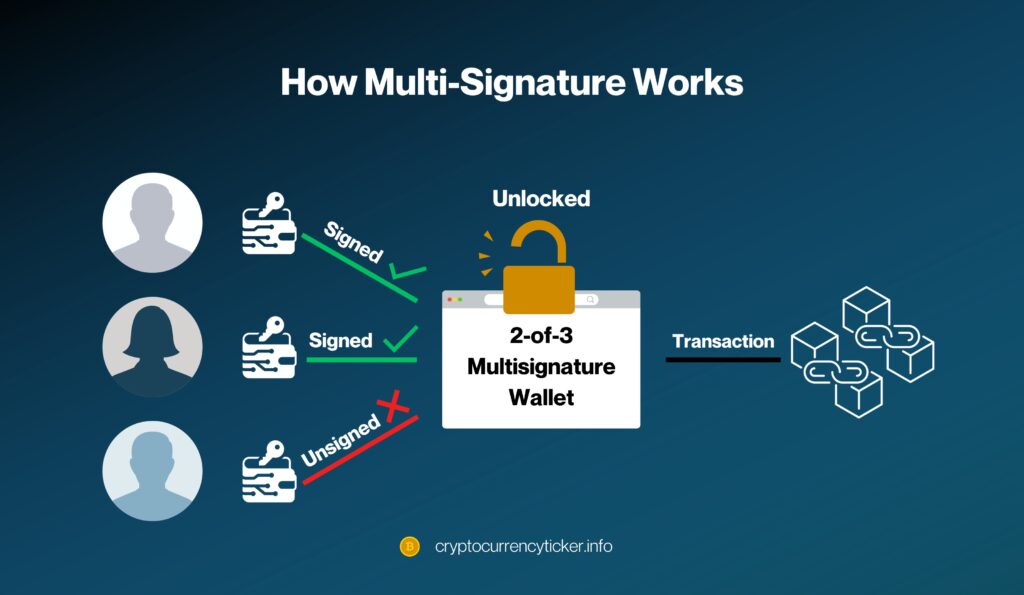
In a standard cryptocurrency wallet, a single private key is enough to authorize a transaction. However, in a multi-signature wallet, transactions require the approval of multiple private keys. This setup can be customized based on the needs of the organization. For example, a 2-of-3 wallet requires two out of three possible keys to sign off on a transaction, providing a balance between security and convenience.
Transaction Process in Multi-Signature Wallets
- Initiation: A transaction is initiated by one of the wallet’s participants.
- Approval Requests: Other participants are notified and asked to approve the transaction with their private keys.
- Transaction Execution: Once the required number of approvals is reached, the transaction is executed on the blockchain.
- Confirmation and Record: The transaction is confirmed on the blockchain, providing a transparent and immutable record.
Technical Considerations
While multi-signature wallets offer enhanced security, they also require a certain level of technical know-how. Understanding key management, transaction verification processes, and wallet configuration are essential skills for anyone managing a multi-sig wallet. This technical requirement ensures that all parties involved are adequately informed and capable of handling their roles in the transaction process.
Enhancing Security: The Multi-Layered Protection Approach
Multi-signature wallets are a paradigm shift in the realm of cryptocurrency security. Their multi-layered protection approach is crucial in mitigating the risks associated with digital asset management. By requiring the consensus of multiple key holders for each transaction, these wallets create a robust defense against unauthorized access and potential security breaches.
Multi-Key Authentication for Enhanced Safety
The cornerstone of a multi-signature wallet’s security is its reliance on multiple approvals for transaction authorization. This structure inherently creates multiple checkpoints, significantly reducing the risk of unauthorized transactions. Even if one key is compromised, the wallet’s contents remain secure, as additional approvals are needed for any transaction to proceed.
Deterrence Against Internal and External Threats
Multi-signature wallets provide a strong deterrence against both internal fraud and external hacking attempts. Since no single person has complete control over the wallet, the likelihood of internal misuse is drastically reduced. Similarly, the complexity of needing multiple keys to authorize a transaction makes it much more difficult for external attackers to access the wallet’s funds.
Security in Collaboration
This approach promotes a collaborative security model. By involving multiple parties in the approval process, multi-signature wallets encourage transparency and collective responsibility. Each participant acts as a check and balance for the others, creating a shared security culture that is much stronger than any individual effort.
Customizable Security Protocols
Another significant advantage of multi-signature wallets is the ability to customize security protocols to fit the specific needs of an organization. The number of keys required for a transaction, the identity of key holders, and the conditions under which they can exercise their rights can all be tailored. This flexibility allows organizations to strike the right balance between security and operational efficiency.
Audit Trails for Accountability
Every transaction made through a multi-signature wallet is recorded on the blockchain, providing a transparent and immutable audit trail. This feature is invaluable for maintaining accountability and integrity within an organization. It ensures that all transactions are traceable and verifiable, reinforcing trust among stakeholders.
Multi-Signature Wallets in Action
The practical application of multi-signature wallets across various organizational structures showcases their versatility and effectiveness. By examining real-world case studies and examples, we gain insights into how these wallets facilitate secure and efficient cryptocurrency management.
Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs)

In DAOs, where decision-making is distributed among members rather than centralized, multi-signature wallets play a critical role. They enable a democratic process for financial decisions, requiring consensus among selected members to execute transactions. This structure not only secures the funds but also aligns with the decentralized ethos of DAOs, ensuring that financial decisions reflect the collective will of the members.
Web3 Corporations
For corporations operating in the Web3 space, multi-signature wallets simplify treasury management while enhancing security. These companies often handle substantial amounts of cryptocurrency and require a secure method to manage these assets. Multi-signature wallets provide a solution that balances security with operational efficiency, enabling multiple team members to oversee and authorize transactions.
Collaborative Projects and Joint Ventures
In projects involving multiple stakeholders, such as joint ventures or collaborative initiatives, multi-signature wallets ensure that all parties have a say in how funds are managed and spent. This setup fosters trust and transparency among participants, as it necessitates agreement from all involved before funds can be accessed or moved.
Non-Profit Organizations and Charities
- Non-profits and charities handling cryptocurrency donations benefit from multi-signature wallets.
- These wallets offer added security and accountability, crucial for organizations where public trust is vital.
- Donors have assurance that their contributions are safeguarded.
- A consensus is required for fund use, aligning with transparency and responsibility principles.
Balancing Control and Collaboration in Team Environments
Multi-signature wallets strike a unique balance between control and collaboration in team environments, revolutionizing how organizations manage their cryptocurrency assets. This balance is pivotal in ensuring that while security is paramount, the flow of operations and decision-making processes remain smooth and inclusive.
Shared Control Promotes Team Involvement
In a traditional single-signature wallet, control is often concentrated in the hands of one individual or a small group, leading to potential risks and a lack of broader team engagement. Multi-signature wallets, by contrast, require input from multiple team members, thereby distributing control and encouraging active participation in financial management.
Enhancing Transparency in Decision Making
The multi-signature model inherently fosters transparency. Each transaction needs multiple approvals, ensuring that financial decisions are not made unilaterally. This transparency is crucial in building trust within the team and with external stakeholders, as it provides assurance that funds are managed responsibly.
Streamlining Operations with Defined Protocols
To effectively implement a multi-signature wallet, organizations need to establish clear protocols outlining who holds the keys, how many approvals are required for different types of transactions, and under what circumstances these approvals are sought. This structure helps streamline operations, providing clarity and efficiency in financial management.
Conflict Resolution and Collaborative Dynamics
Multi-signature wallets also introduce a unique dynamic in conflict resolution. Since no single individual can dominate decision-making, teams are encouraged to discuss and resolve disagreements collaboratively. This aspect can be particularly beneficial in preventing impulsive or risky financial moves, as consensus must be reached before any action is taken.
Preparing for Challenges in Key Management
While multi-signature wallets offer many benefits, they also pose challenges, particularly in key management. Loss of a key or disagreements among key holders can lead to operational hurdles. Therefore, it’s crucial for teams to have contingency plans and clear guidelines on handling such situations, ensuring the smooth functioning of the wallet.
The Technical Aspect: Setting Up and Managing Multi-Signature Wallets
Implementing and managing multi-signature wallets involves a blend of technical understanding and practical know-how. This section delves into the essentials of setting up these wallets, ensuring they are configured correctly to serve the specific needs of an organization or team.
Setting Up a Multi-Signature Wallet
Setting up a multi-signature wallet involves several key steps:
- Choose a reputable wallet provider based on security, user interface, and cryptocurrency compatibility.
- Determine the number of required signatures, balancing security and practicality.
- Assign keys to trustworthy team members who understand their role in security.
- Follow the provider’s instructions to create the wallet, generating keys and configuring settings.
- Test the wallet before significant transactions to ensure everything works correctly, especially multi-signature features.
Managing the Wallet
Once set up, effective management of a multi-signature wallet is key to its success:
- Regular Audits and Reviews: Periodically review the wallet’s activity and audit the transaction history to ensure compliance with the organization’s protocols.
- Updating Access as Needed: In response to team changes, update the wallet’s access controls and key distributions accordingly. This step is crucial to maintain security and operational efficiency.
- Training and Educating Team Members: Ensure that all key holders are adequately trained and understand the importance of their role in managing the wallet. Regular training sessions can help in keeping the team updated on best practices and security protocols.
- Preparing for Contingencies: Have plans in place for scenarios like key loss or a team member leaving. This preparation can include backup keys or protocols for redistributing keys when necessary.
- Monitoring for Security Threats: Stay vigilant for potential security threats or vulnerabilities. Keeping the wallet software updated and following industry best practices for cybersecurity can mitigate these risks.
Pros, Cons, and Considerations for Organizations
Adopting multi-signature wallets in an organizational setting comes with its set of advantages and challenges. Understanding these pros and cons is essential for any entity considering integrating multi-signature technology into their cryptocurrency management strategy.
Advantages of Multi-Signature Wallets

- Enhanced Security: Multiple approvals reduce fraud risk, ensuring top-tier security.
- Increased Accountability: Multiple stakeholders reduce fund mismanagement possibilities.
- Operational Resilience: Distributed key management prevents single points of failure.
- Transparent Transactions: Blockchain records and multiple approvals ensure transparency.
- Customizability: Tailor wallets for specific organizational needs, like different transaction thresholds.
Challenges and Considerations
Complexity in Setup and Management: Multi-signature wallets can be technically challenging, demanding expertise for setup and management.
Operational Delays: Multiple approvals may cause transaction delays when key holders are in various time zones or unavailable.
Risk of Key Loss or Mismanagement: Losing one key in multi-signature can complicate fund access, and mismanaging keys by a signatory poses security risks.
Potential for Internal Conflicts: Consensus in multi-signature wallets can spark internal conflicts, especially in high-stake decisions.
Ongoing Maintenance and Security: Regular monitoring and maintenance are needed for wallet security, which can be resource-intensive.
Weighing the Decision
Organizations should carefully weigh these pros and cons when considering multi-signature wallets. Consider factors like organization size, transaction scale, team technical skills, and the trade-off between security and operational speed. In many cases, the benefits of enhanced security and accountability outweigh challenges, especially for organizations with substantial crypto assets or a need for transparency and collaborative decision-making.
Conclusion
The exploration of multi-signature wallets reveals their critical role in enhancing the security and efficiency of cryptocurrency management for teams and organizations. By requiring multiple approvals for transactions, these wallets introduce a robust layer of security, greatly mitigating risks associated with digital asset management.
The transparency, accountability, and collaborative decision-making fostered by multi-signature wallets align perfectly with the needs of modern organizations, especially those operating in decentralized or distributed environments. While they do present certain challenges, such as technical complexity and the need for consensus, the benefits in terms of enhanced security and shared control are substantial and often outweigh these considerations.